What do you need to know about solid waste management in the Philippines?
Start with these questions and statistics!
More Articles on Urban Solid Waste Management in the Philippines
How much waste does the Philippines produce yearly?
18 Million tons!
The Philippines was estimated to generate 18.05 Million Tons in 2020, according to the latest Solid Waste Management Status Report (2008-2018)
That’s equivalent to the weight of more than 2 MILLION ELEPHANTS!
This figure may be an underestimation, as it does not account the COVID-19 pandemic.
Total solid waste generation of the Philippines is expected to reach 23.61M tons in 2025.
The NSWMC now hosts a dashboard for projected waste generation by city and municipality in the Philippines.
How much waste does an average Filipino produce?
In the Philippines, a person generates around 0.40 kg daily.
To compare, in Singapore, a person generates 3.72 kg of solid waste daily (otherwise known as daily per capita generation).

Read: Cities of the Philippines and Waste Management: Waste Generation of Philippine Cities
What can affect a person’s waste generation?
Daily waste generation of a person may be higher (or lower) with changes in lifestyle, urbanization level, and migration patterns.
5 Most Important Questions about PH Solid Waste Management
What types of waste are generated in the Philippines?
52% of the solid waste generated in the Philippines is biodegradable, as of 2015.
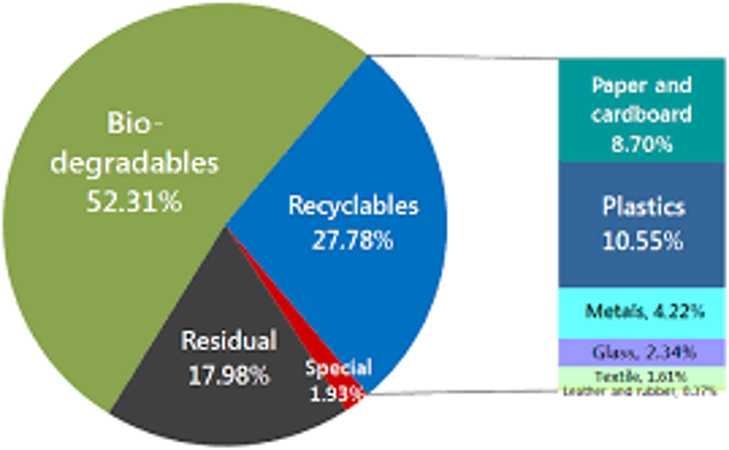
With proper composting, especially backyard composting, a significant volume of waste can be reduced from management.
However, the because Philippine cities are planned poorly, backyard composting is a challenge.
Read: 3 Reasons Why Urban Solid Waste Management is Important!
In the Philippines, where do municipal solid wastes come from?
Most of solid waste that Filipinos generate come from residential sources – 57% of it!
These are in the form of kitchen scraps, yard waste, paper, and plastic, among other types of waste.
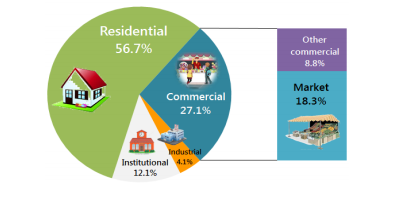
Because residential sources generate a major percentage, municipal solid waste management should focus on reducing waste generation by households.
Although industrial solid waste consist only 4% of total Philippine solid waste, managing it requires much effort and resources.
How many years has the Philippine waste management law been in effect?
21 years. The age of Republic Act 9003, the landmark law, as of January 2022.
RA 9003 is a declaration to “adopt a systematic, comprehensive and ecological solid waste management program.”
Three presidents – Macapagal-Arroyo, Aquino, Duterte – were not enough to achieve the salient conditions of Republic Act 9003, particularly waste segregation at source.
In January 2021, the Philippine Institute of Development Studies published a discussion paper on the regulatory policies of Philippine solid waste management.
WATCH: We Overlook THIS in Solid Waste Management
Does the Philippines recycle?
A Rappler article reports that, as of 2016, only 5% of total Philippine waste is recycled.
50% is the target waste diversion rate of the incumbent National Solid Waste Management Strategy (2012-2016).
Waste diversion are “activities which reduce or eliminate the amount of solid waste from waste disposal facilities (RA 9003).”
These include reduction of waste at the source, recycling and composting.
Latest available data of 2015 suggests that average diversion rate in Metro Manila is 48% while outside Metro Manila is 46% (although many LGUs report lower.)
How many barangays have material recovery facilities?
32% of total barangays in the Philippines are served by material recovery facilities (MRFs) as of 2018.
Out of the 42,044 barangays in the Philippines in 2018, 13,612 were served by MRFs (NSWMC Report 2008-2018).
Republic Act 9003 defines material recovery facilities as a facility “designed to receive, sort, process, and store compostable and recyclable material efficiently and in an environmentally sound manner (Section 33).”
The law does not mandate individual barangays to operate individual MRFs. Facilities can be shared among clusters of barangays.
Here are my past projects in local government planning…
Have people been punished for violating the provisions of the solid waste management law (Republic Act 9003)?
A December 2020 Municipal Trial Court Decision found an elected official in Region 3 (Central Luzon) guilty of violating provisions on the establishment and operation of open dumps (Section 48 (9)).
Sentence is a fine of P500,000 and 5% of net annual income for the year 2010.
600 local government executives were investigated by the Ombudsman through complaints filed by the Ecowaste Coalition on February 2016.
The progress of the investigations manifest that local governments are being made accountable for failure to implement proper solid waste management systems.
Read: How can we make solid waste management more convenient?
How much of Philippine waste is plastic waste?
10% of total waste generated by the Philippines is plastic waste, according to a 2019 PhilStar article.
It is good that plastic waste is receiving worldwide attention because it is really a difficult material to dispose.
However, other types of waste are not receiving as much attention, e.g., food waste and paper waste.
Do local governments in the Philippines plan solid waste management?
Philippine provinces, cities and municipalities are mandated by law to prepare 10-year solid waste management plans.
2021 UPDATE: The NSWMC now hosts a dashboard of the 10-year solid waste management plans of Philippine LGUs.
As of November 17, 2021, 65.3% of all LGUs have approved solid waste management plans. Still under evaluation are 30.4% of LGU SWM plans; around 4% have not submitted SWM plans for approval.
LISTEN: How do LGUs in the Philippines plan solid waste management??
How is waste disposed in the Philippines?
The Philippine Ecological Solid Waste Management Law mandates sanitary landfills as “alternative final disposal sites” to open and controlled dumpsites.
Sanitary landfills have “engineering control over significant potential environmental impacts.”
In 2018, only around 22% Philippine local government units have access to sanitary landfills.
Local government units are not required to establish their own sanitary landfills. (The NSWMC has a list of operational sanitary landfills.)
Common waste disposal facilities, and waste management facilities in general, can be shared, pursuant to the Cooperative Undertakings provision of the Local Government Code (Section 33 of Republic Act 7160.
In 2018, there were still 353 illegal dumpsites operating (NSWMC).
All dumpsites should have been closed and phased out in 2006.
In August 2021, DENR reported that all open dumpsites have been shut down.
The Closure of dumpsites is one of my top stories for 2021 Rewind!
Does waste management affect climate change?
In 2018, the Philippine waste sector was estimated to contribute 6% of the total human-induced greenhouse gas emissions of the country.
The solid waste sector contributes to human-induced GHG emissions mainly through collection and disposal processes.
- Garbage trucks run on fossil fuel.
- Waste diversion facilities have machines that emit smoke.
- Backyard burning becomes harmful as waste content includes plastic waste.
Incineration is prohibited in the country through the Clean Air Act (RA 8749), so waste-to-energy (WTE) is being pursued.
However, the pursuit of WTE technologies is also deemed a loss scenario by waste campaign groups.
We proposed policy roadmaps for smart solid waste management
How much do local governments spend on waste management?
According to What a Waste 2.0, high income countries spend 4% of total municipal budget on solid waste, middle-income countries 11%, and low-income countries 19%.
The Philippines is classified as a lower-middle-income country.
Municipalities in developing countries like the Philippines typically spend 80-90% of their total municipal solid waste budget spent on collection and disposal services, based on a 2013 study of developing countries.
Reducing generated solid waste will also reduce the needed budget for collection and disposal.
A model in waste collection budget is San Fernando City, Pampanga, which has reduced its waste management expenditure from P70M to P15M.
What tools and instruments are available to LGUs in planning waste management?
How can scavengers help improve municipal waste management systems?
A 2012 study found that in Quezon City, the informal sector recovers 30% of total municipal solid waste.
The informal sector refers to scavengers, waste pickers, and other individuals who are “involved in the extraction of recyclable and reusable materials from mixed waste (Wilson 2006)”.
The informal sector has been argued to be an important component of the solid waste management system, particularly by a 2012 study in Iloilo City.
While the activities of the informal sector provide enhanced income opportunities for the poor, they are not always integrated in waste management strategies.
Enroll in my course on solid waste management…
Further Reading
- National Solid Waste Management Status Report (2008-2018)
- PAGE: Urban Solid Waste Management in the Philippines
- What a Waste 2.0
Interested in solid waste management planning?

2 replies on “15 Statistics about Solid Waste Management in the Philippines that Every Filipino should Know (Updated 2022!)”
Good read.
Thank you! Your comment means a lot, and I would like your feedback on future posts.